Understanding Infertility in the U.S.

Understanding
Infertility in the U.S.
What is
Infertility?
Infertility is a disorder of the male or female reproductive system defined by the failure to achieve a clinical pregnancy after 12 months or more of regular unprotected sexual intercourse.8 It is an increasingly common and potentially devastating condition that doesn’t discriminate by race, gender, sexual identity, or socioeconomic status.
Infertility rates in the U.S. continue rise due in part to:
Hopeful parents deciding to have children later
Environmental factors (medication and toxins)
Lifestyle factors (smoking, alcohol, drugs, obesity, stress)
Genetic abnormalities
Sexually transmitted infections
Access to sexual and reproductive health services
Millions of Americans
experience infertility.1
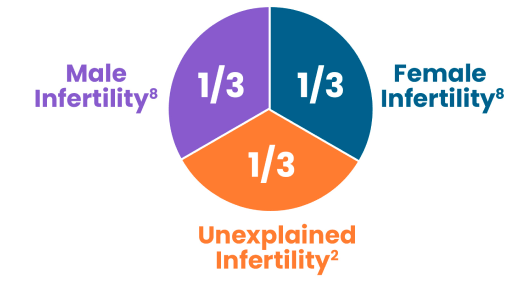
Causes of infertility
among men:
Testosterone treatment77
Disruption of testicular
or ejaculatory function9
Cancer treatment9
Medical conditions9
Hormonal disorders9
Genetic disorders9
Causes of infertility
among men:9
Testosterone treatment
Disruption of testicular
or ejaculatory function
Cancer treatment
Medical conditions
Hormonal disorders
Genetic disorders
Causes of infertility
among women:9
Disruption of
ovarian function
Effects of ovarian ‘age’
Fallopian tube obstruction
Physical characteristics
of the uterus
Who is affected?
35%
of men
Over one-third of men in the U.S. have low sperm count impairing conception rates.11
1 in 5
women
Twenty percent of married U.S. women of child bearing age, with no prior births, are unable to get pregnant after a year of trying.10
60%
of couples with
high BMI
Couples in which both
members have a Body
Mass Index (BMI) over 35
experience 60 percent
lower fertility than
couples in which both
partners have a healthy
BMI under.15
69%
of cancer
patients
Over two-thirds of
individuals of
reproductive age
diagnosed with
cancer require fertility
preservation
procedures and
services.16


