IVF Access
at Risk

Why IVF Access
Is at Risk
Who is regulating
fertility treatments?
The field of assisted reproductive technology (ART) has evolved over the past four decades to regulate practices, protect patients, and represent all involved parties. Today, a wide range of government and professional organizations oversee fertility treatment and testing.
Federal
Oversight
FDA
U.S. Food and Drug Administration controls approval and use of drugs, biological products, and medical devices and has jurisdiction over screening and testing of reproductive tissues.
CDC
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention collects and publishes data on assisted reproductive technology (ART) procedures.
CMS
The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services is responsible for the implementation of the Clinical Laboratory Improvement Act to ensure the quality of laboratory testing.
Professional
Society
Oversight
CAP
College of American Pathologists administer a reproductive laboratory accreditation program from embryology labs.
SART
Society for Assisted Reproductive Technology monitors fertility clinics for adherence to ASRM guidelines, accreditation of their embryology labs, qualification of their staff, and submission of data to the CDC.
JCAHO
Joint Commission on Accreditation of Healthcare Organizations regulates ART laboratories in hospital and has the authority to inspect ART laboratories that are located outside of hospitals.
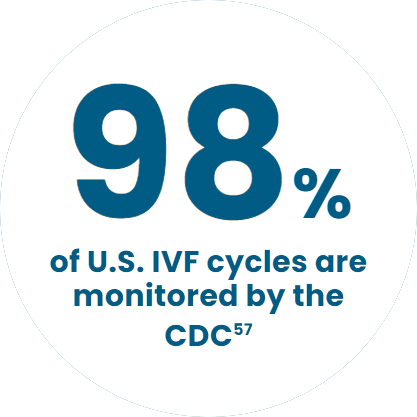
98% of U.S. IVF cycles are monitored by the CDC57
The CDC collects and reports data on ART (assisted reproductive technology) procedures in the United States to monitor outcomes, improve patient safety, and enhance understanding of reproductive technologies.

The debate over IVF
Despite stringent federal oversight designed to ensure ART (assisted reproductive technology) safety and the proven success of in vitro fertilization in helping overcome infertility issues, special interest groups lacking clinical expertise in IVF are seeking to drastically limit or eliminate access to this crucial treatment. Their current efforts are focused on:
- Restricting genetic testing, leading to an increased risk of miscarriages
- Limiting the number of embryos created which will lower success rates
Myths surrounding IVF
Opposition to IVF and other ART (assisted reproductive technology) procedures is largely fueled by a disinformation campaign that spreads outdated myths and misinformation about the facts and science of fertility.
Misconception
1 embryo = 1 life.
Reality
Special interest groups are intentionally misleading the public by labeling every embryo as a life. Only 40-60% of embryos — from both natural conception and IVF — result in live births.36

Myths surrounding IVF
Opposition to IVF and other ART (assisted reproductive technology) procedures is largely fueled by a disinformation campaign that spreads outdated myths and misinformation about the facts and science of fertility.
Misconception
Millions of embryos are created and either destroyed or abandoned.
Reality
Irresponsible anti-IVF groups fail to distinguish between viable and non-viable embryos.
In young women with normal fertility, up to 70% of embryos are lost due to implantation failure, early pregnancy loss, or miscarriage.60
For infertile or subfertile couples, this inefficiency is even greater, with up to 20 embryos needed to achieve a live birth.53,63

Myths surrounding IVF
Opposition to IVF and other ART (assisted reproductive technology) procedures is largely fueled by a disinformation campaign that spreads outdated myths and misinformation about the facts and science of fertility.
Misconception
Preimplantation genetic testing (PGT) is unnecessary, and clinics are practicing eugenics.
Reality
Extensive evidence shows that preimplantation genetic testing for aneuploidy (PGT-A), increases live birth rates, and lowers clinical miscarriage rates.63,83,84,85

Myths surrounding IVF
Opposition to IVF and other ART (assisted reproductive technology) procedures is largely fueled by a disinformation campaign that spreads outdated myths and misinformation about the facts and science of fertility.
Misconception
Limiting clinics and patients to three embryos has worked in other countries.
Reality
In 2004, Italy enacted a law that:
- Set a limit of three embryos per cycle
- Required physicians to implant all resulting embryos at one time
- Prohibited cryopreservation
- Prohibited genetic testing
In 2009, Italy’s Constitutional Court reversed most of these laws, and in 2012, the European Court of Human Rights removed the remaining restrictions.

Myths surrounding IVF
Opposition to IVF and other ART (assisted reproductive technology) procedures is largely fueled by a disinformation campaign that spreads outdated myths and misinformation about the facts and science of fertility.
Misconception
Embryo protection legislation is working in states like Louisiana.
Reality
Louisiana banned the destruction of any “viable embryos,” but the law’s definition of viability differs from the medical community’s.
This discrepancy exposes IVF providers to criminal charges and lawsuits, leading to a 33% decrease in IVF clinics over five years.65,66
Louisiana ART (assisted reproductive technology) births is now 1.3% per year vs. the national average of 2.3%.71
Restrictions on embryo and eggs can compromise IVF success rates
In IVF, having more eggs collected can lead to better birth outcomes. If patients have extra embryos stored, they are less likely to need more rounds of egg retrieval, which can be expensive, inconvenient, and invasive.69


